Electric cars – the ultimate guide
Last updated: March 15th 2024
Electric cars (also known as EVs) will transform the car industry and will begin to dominate our roads in years to come.
A study in the 2018 Journal of Applied Energy showed that electric cars are cheaper to run than their fossil fuel alternatives (also known as Internal Combustion Engine, or, ICE vehicles) and can outperform them too. Electric and AFVs (Alternative Fuel Vehicles) can go as fast as most supercars, and are vastly more energy efficient than their fossil fuel equivalents.
This guide covers the important elements of electric car ownership. For further reading, check out how to sell an electric car. If you’re ready to sell your electric car, you can start with Motorway now.

London’s ultra-low emissions zone (ULEZ) was first introduced in April 2019. Since then, more LEZs have been introduced country-wide, and despite the policy changes, the popularity of high-polluting diesel and petrol cars is falling. Instead, more and more people are turning to electric vehicles (EVs).
In January 2024, the Zero Emission Vehicle Mandate (ZEV) was introduced. This mandates car manufacturers to ensure that 22% of their new car sales in 2024 are zero emission (and 10% of van sales have to be zero emission), with an increasing percentage of EV sales required each year up to 100% in 2035. This is in line with the goal of restricting new car sales from 2035 to be all-electric only.
In this electric cars ultimate guide we’ll look at the following:
- How do electric cars work
- How long does it take to charge and electric car?
- How much is an electric car?
- How much is car tax (VED) for an electric car?
- How much is insurance for electric cars in the UK?
- How much are maintenance costs for electric cars?
- How much do electric car charging stations cost?
- How do you charge an electric car?
- How many miles can an electric car go without stopping?
- How fast are electric cars?
- Are electric cars better for the environment?
The rise of electric cars
Electric cars have been around since the early 1800s, but they never quite took off until this century. This is solely because they have been totally outperformed on almost every measure by petrol and diesel alternatives. Electric cars used to be too inefficient, expensive to run, slow, and simply not comparable to other models in terms of performance.
We’ve seen increasingly more electric cars on the road in recent years. Stand-out models include the BMW i3 and Tesla Model 3. With electric vehicles becoming a viable option for more motorists every year, we’re here to shine some light on the topic.
How do electric cars work?
Instead of the engine burning a fossil fuel like diesel or petrol, electric cars run on electricity. They contain big internal batteries that you charge, instead of filling up with traditional fuel. Recent improvements in battery technology have made EVs just as viable for daily or weekly driving as ICE vehicles.
Most EVs operate from a high-voltage lithium-ion battery. Unlike the ‘normal’ batteries in most cars, which are primarily used to power things like the radio and start the engine, the battery in an electric car runs everything including the motor.

How long does it take to charge an electric car?
Electric cars can take as little as 30 minutes to charge, or more than 12 hours.
Currently, most public charging points are Level 2 and 7kW. Depending on your EV, it can take up to 10 hours to fully charge your vehicle using these chargers. Public ‘power chargers’ exist and can partially or fully charge EVs much quicker than the Level 2s.
Tesla sells an at-home charge point (a wallbox) which works on 22kW for speedy at-home charging. Power charging and long ranges are all possible because of advances in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries can provide up to 620 miles on one full charge and have a very high energy density. They are less likely to lose their charge when not in use and are lightweight meaning they’re great to have under the bonnet or chassis.
Read our guide to find out exactly how long it takes to charge EVs.
How much is an electric car?
Many car brands are branching out into EVs, and most are starting with small models that cost between £15,000 and £28,000. Some are also producing higher-end SUVs for drivers who want the benefits of electric with the comfort of a luxury vehicle. There are now enough electric cars on the market for most drivers to find a suitable model within budget.
From 1st April 2025, EVs will be subject to road tax including the expensive vehicles supplement. So, if you spend more than £40,000 on your EV you can expect to pay hundreds of pounds in road tax for at least the first five years of ownership.
When sizing up the price of any car, you need to think about purchase price and running cost. A study conducted by the International Council on Clean Transport found that electric cars are cheaper to own and run than ICE vehicles in five European countries.
The study examined the purchase, fuel and tax costs of Europe’s best selling car at the time, the VW Golf, in its electric, hybrid, petrol and diesel versions. Over four years, the pure electric version was the cheapest in all places – UK, Germany, France, Netherlands and Norway. This was put down to a combination of lower taxes, fuel costs and subsidies on the purchase price.

How does electric car salary sacrifice work?
Salary sacrifice can help you save between 30-60% on the cost of an electric car. Under a salary sacrifice scheme, money for your chosen employee benefit (in this case, your car) is taken from your gross salary before any income tax or national insurance contribution is deducted. Learn more about salary sacrifice schemes here.
Are electric cars worth it? Pros and Cons
There are many advantages to owning an electric car. Here are our top 5:
1) Fuel is up to 5 times cheaper
Electricity for your car will cost you up to 5 times less than fuel for your petrol/diesel car. Of course, this is subject to fluctuations in fuel costs.
2) They are better for the environment
They don’t use fossil fuels and therefore have a much smaller carbon footprint than their fuel-based cousins.
3) You pay no tax until 2025.
There’s no road tax (VED) to pay in the UK for electric vehicles until 2025.
4) They are fun to drive
Electric car motors are fundamentally different from the internal combustion engine and this makes for a totally novel driving experience. Acceleration is often much quicker.
5) Quieter driving experience
Electric engines don’t have any fuel to burn and combust, which makes them a lot quieter to drive.
What are the main disadvantages of owning an electric car?
Like all things in life, EVs do have some downsides:
1) Inconvenience: you have to wait for them to charge
Depending on the type of charger you are using (and the size of your car’s battery), it can take anywhere between 30 minutes and 12 hours.
2) Cost: insurance can be more expensive
EVs tend to be higher value, meaning they are more expensive to insure just like high-value combustion vehicles, such as Porsche or BMW.
3) Cost: maintenance can be more expensive
EVs require specialist knowledge to service and maintain
4) Cost: purchase price
The Volkswagen Golf petrol engine model starts at around £25,000 for the most basic model. The e-Golf starts at approx £31,000 – so electric cars can come at a comparative premium.
5) They weigh more
These vehicles rely totally on the battery, these are often large and linked together in arrays or packs. This can weigh a lot and reduce the car’s range.
How much is car tax (VED) on electric cars?
All fully-electric vehicles are totally exempt from vehicle excise duties (also known as car tax, or simply VED) until 2025. Read more about road tax for EVs here.
Hybrid vehicles (a mixture of electric and fuel) will be tax-free as long as they have zero C02 emissions; so your tax cost will vary from model to model.
If you live in London, you won’t have to pay the congestion charge or ULEZ charge on an electric vehicle.
How much is Insurance for electric cars in the UK?
Insurance on EVs is found to be higher than insurance on ICE vehicles. In 2023, the Association of British Insurers (ABI) defended the higher premiums by saying they are based on risk. Through data collected by the ABI, it was found that claims for EVs are 25.5% more expensive compared with their internal combustion engine equivalents. EVs are also taking 14% longer to repair which also impacts premiums.
How much are maintenance costs for electric cars?
Electric vehicles (EVs) are generally cheaper to maintain than fossil fuel vehicles, as much as £600 cheaper if you charge it at home. This is due to the fact that most EVs have fewer working parts than a standard internal combustion car. Whilst this means that that is less that can go wrong, EVs still need regular servicing in order to run efficiently.
Additionally, any niche or highly specialist repairs could be more expensive than in a traditional car, since not all mechanics are trained in servicing EV engines.

How much do charging stations for electric cars cost? Calculate electric car charging costs.
Going electric will save most car owners a lot of money on fuel costs.
Many estimates consider the cost of charging your electric car to be around five times cheaper than using a petrol or diesel car fuel equivalent. You can also charge your electric car at home, meaning you never need to go to the petrol station again!
The Energy Saving Trust estimates that charging your car from home costs around £2 to £4 for every 100 miles.
How do you charge an electric car?
Charging electric vehicles is often a worry for many potential EV owners and the process is frequently misunderstood. But don’t fear, it’s all pretty simple. When it comes to charging your EV you have two options:
A) Charge your car at home
B) Charge your car at a public charging point.

How do I charge my electric car at home? (home charging stations)
This is the best option for charging if you have a driveway or street parking outside your home. If you don’t have parking at home then you may want to see the section below on charging whilst on the road.
There are two ways to charge your electric car from home.
Charge via the mains, like you would your mobile phone (this is slow)
Charge via a specialist home charging point (this is fast!)
Charging via the mains (3-pin)
All electric vehicles come with the correct cables and accessories to allow you to charge your car from home via the mains right off the bat. One end goes into the mains with a normal plug, just like the one on your kettle.
The other end goes into the charge point on your vehicle. This is known as ‘trickle charging’ and it can be slow.
For example, charging a Nissan LEAF to full (the UK’s most popular EV) could take between 12-15 hours.
With an upgraded 7KW charging point, you can get your charging time down to 4-5 hours.
Charging with a home charging station
Having a car charger can decrease the time it takes to charge your EV by up to 10 times. They also increase safety as there is no need for cable trailing around your house. All you have to do is order one and have it installed at a dedicated point (usually, next to where you park your car). Unfortunately, there is an initial installation cost of up to £1,000.

There are many variations available on the market. Which one you choose will depend on the vehicle you own. Pod Point, a popular seller of home charging points, offers three options: 3.6kW, 7kW, and 22kW.
The higher the kW, the faster your battery will charge. You will need to check whether your electric car is compatible with high kW charging before deciding which option to go for.
You can use the Pod Point website’s tool to help you find out which charging point is right for a particular vehicle.
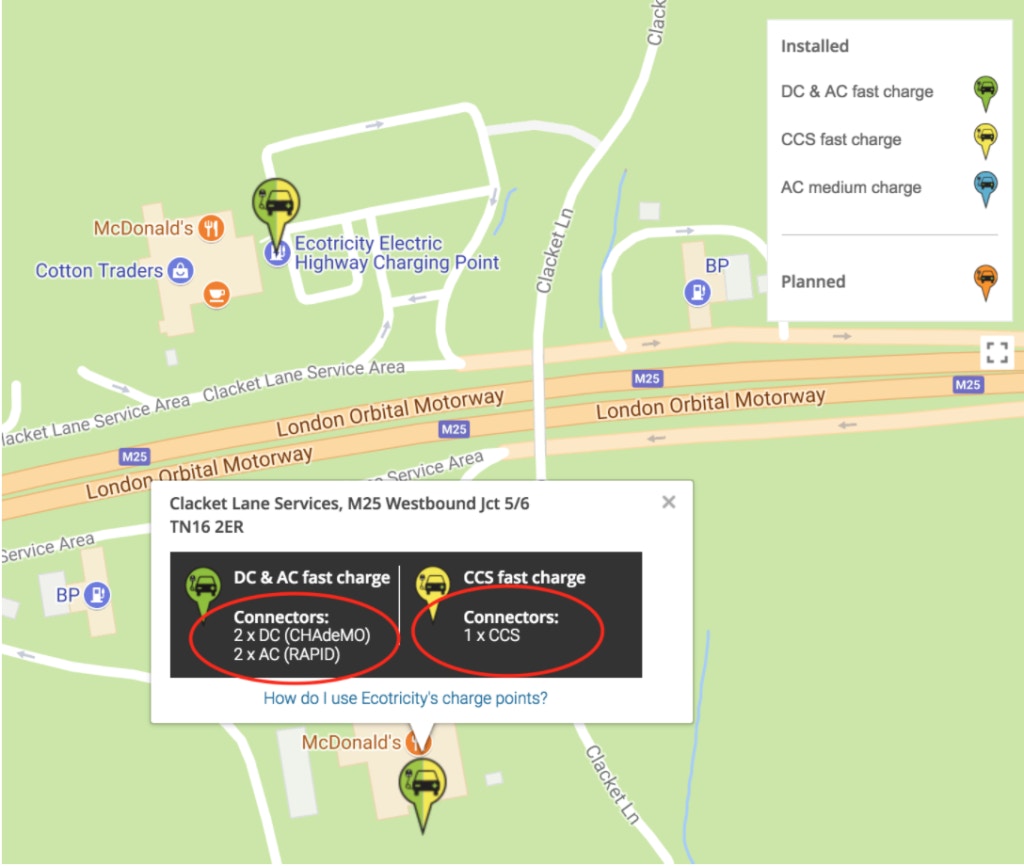
In the example below, we checked a Tesla Model S and then selected the option with a cable.

It shows that this particular EV will work with the highest kW charger available (22kW) and will charge to full in 4 hours.
How do I charge my electric car at public charging points and stations in the UK? (and where to find them)
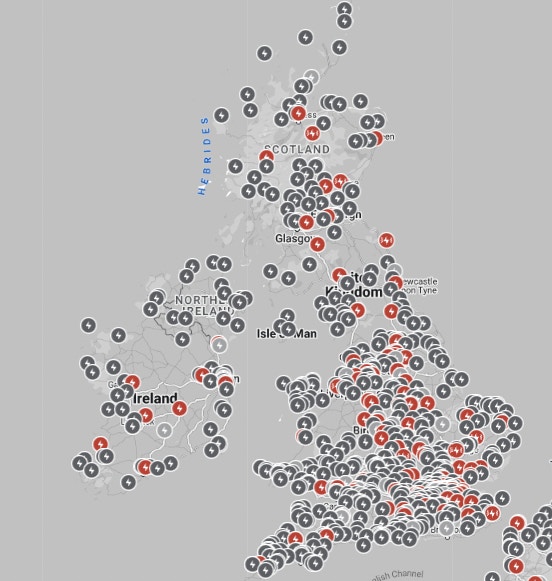
If you need to charge your EV away from home there are plenty of charging points around the UK. Zap-Map provides a great map tool for locating your nearest charging point.
You can just tap on a particular point to see information about who is providing the power and any costs. They also have a very handy app. As you can see from the image below, there are already plenty of options all over the UK!

Pro tip: many electric cars now come with a smart GPS that will direct you to the nearest charging point.
With the government having announced it will spend £400m on a national charging network, this infrastructure is only set to grow. Most charging points these days provide free ‘slow’ charging but many different providers may ask you to pay for ‘fast’ or ‘rapid’ charging.
Some providers may also require you to download an app or start a subscription to access charging. You can find more information about the different charging providers and costs on Zap-Map.
How do I charge an electric car at service stations? (and petrol stations)
The number of rapid charging points at service stations is increasing every day and the trend is only set to continue; especially with big players like Shell starting to compete by introducing electric charging points at their petrol stations.
Currently, the Ionity network charges £0.69 per kWh. So, a 100kWh EV sets you back £69 for a full charge. Cars that cover five miles per kWh will pay around 13.8 pence per mile using Ionity. The chargers on the Instavolt network are slightly cheaper – at £0.66 per kWh.
Osprey rapid chargers cost around £0.79 per kWh – so, a 100kWh EV would cost around £79 for a full charge. bp pulse charges around £0.44 and £0.69 – the range of prices depends on the speed of the charger being used, and whether you have signed up to the app or not.
What are Tesla charging stations? (Tesla supercharger network)

Tesla now has its own charging infrastructure, for Tesla cars only, in place across the UK and around the world.
The Supercharger network is the fastest in the UK with speeds of up to 120kW available (about five times as fast as your standard public charger). It will take around 30 minutes to get to 80% charge.
They operate two different networks, Supercharger (for rapid charging on the UK’s major roads) and Destination (for charging in towns/cities and places drivers are likely to spend their time). Destination charges are free to use by all Tesla owners.
In 2022, Tesla rapid chargers cost 44p/kwh which works out at around £11 for 30 minutes of charging. However, the Tesla Supercharger Network also has points across the UK which are free to use for owners of Tesla EVs.
Touchscreen navigation systems inside every Tesla model can navigate you to the nearest Supercharger station or unit. Simply enter a destination on your touchscreen and ‘Trip Planner’ will give you the best route through Superchargers along the way.
You won’t need a smartphone app or card to charge your Tesla at a Supercharger or Destination point. The unit will communicate with the car to make sure the vehicle is a Tesla before allowing you to charge. Below is a map of all the charging points currently in the UK (Supercharger in Red, Destination in Grey).
How many miles can electric cars go without stopping?
In 2022, the average distance an EV can go on a single charge is 193 miles. However, there are electric vehicles that can go up to 300 or 400 miles on a single charge.
Charging infrastructure is also growing rapidly, so if you’re in a town or city it shouldn’t be hard to find somewhere to park and charge your car if you run out of range.
Range can also be extended if you drive efficiently. This is similar to petrol and diesel vehicles. If you keep the pedal to the metal for long periods, do fast starts and lots of stop-starting, your battery will run down faster.
How do I get the maximum range from an electric car?
Maintain momentum
Read the road ahead and reduce unnecessary acceleration and breaking.
Avoid braking harshly
Regenerative braking is a key feature with EVs. When you lift your foot from the accelerator, resistance (kinetic energy) is created, this is then used to recharge the battery while you drive. Harsh braking will reduce this process and lead to your battery running down faster than it might usually.
Keep it slow and steady
High speeds will increase energy consumption more in an electric vehicle than it will do in a traditional petrol/diesel model. This is because EVs don’t have gears and the energy saved by driving at high speeds in a high gear won’t apply to an electric.
Be conservative with the heating and air-con
Heating and air conditioning can add up to 10% on the total amount of energy withdrawn from the battery on an EV. Air conditioning will use up less power but if you’re travelling at low speeds it may save you a few quid to open the window instead.
Know your vehicle’s eco features
Lots of the latest EVs come with features that can save you power and money, so make sure to read the handbook for your model for specific information.
How fast are electric cars?
Electric cars typically have much faster-starting acceleration than their fuel-based counterparts. This is not because they are more powerful per se but because the power is available earlier than a fuel-based vehicle.
The Tesla Roadster claims to hit 0-60mph in 1.9 seconds and 0-100mph in 4.2 seconds (times achieved by F1 cars), a quarter of a mile takes just 8.9 seconds.
That’s the fastest time ever recorded for a production car. This would embarrass most Lamborghinis, Ferraris, and Porsches from a standing start. Top speed isn’t an issue either, with the Roadster coming in at 250mph.
Generally, though, top speeds are slightly lower on most electric models, the fast acceleration notwithstanding.
A good demonstration of electric cars being quicker off the line but slower at top speed can be found in this amazing video of a Tesla Model S vs the McLaren 720S.
What are hybrid cars?
Hybrid cars use both electric and petrol or diesel power. This means combining a petrol or diesel engine with an electric motor. They consume less fuel and emit less C02 than a comparable all-fossil fuel model.
They are, in general, cheap to fuel, with better fuel economy than all-fossil fuel cars. Owners also benefit from lower first-year VED (road tax) as well as avoiding congestion charges.

An extremely popular hybrid model is the Toyota Prius.
The Prius has traditionally been used by many ride-sharing drivers (like Uber) in urban centres, as it’s very economical for city driving. When going at low speeds with lots of stop-starting, only the electric motor is used.
Hybrids offer the best of both worlds. Unlike electric cars, the downside of hybrids is that they still pollute (although not as much as standard petrol/ diesel cars).
To refuel them, you fill the tank with petrol or diesel at a filling station, like with any all-fossil fuel vehicle. The electric motor charges itself through regenerative braking and the engine itself.
Are electric cars better for the environment?
Electric cars still use electricity that may have been produced by burning fossil fuels, but estimates suggest that even if this is the case, they cut over half the emissions an internal combustion engine produces.
If the electricity is produced by nuclear or hydropower, the emissions footprint of the vehicle can be as little as 1% of a traditional combustion engine. We can safely advise that electric cars are much better for the environment. They should prove to be a very good investment, particularly in urban centres.
Ready to sell your car?
Ready to learn more about valuing, maintaining, and selling your car?Check out more of our guides here, covering everything from hybrid and electric car depreciation, to converting your car to dual-LPG fuel. With 84% of Motorway customers getting more money, it’s never too soon to get your valuation.
- Selling an electric car – ultimate guide
- LPG cars: the ultimate guide
- Van valuation – the ultimate guide
- Hybrid cars – should you sell?
- London’s ULEZ – ultra low emission zone
- Birmingham Clean Air Zone
- Sell your car with Motorway
- Sell your electric car or EV with Motorway
- Do electric cars pay the congestion charge?
- How & where to charge your electric car at home and on the road
- How long does it take to charge an electric car?
- What is a hybrid car and how do they work?
- Do electric cars need servicing?
The information provided on this page is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice.